Advanced Integrated Manufacturing
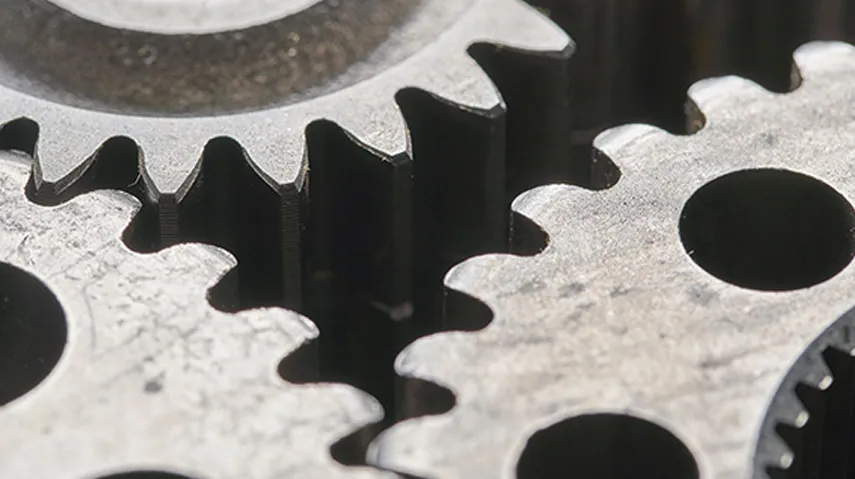

Mid’s Advanced Integrated Manufacturing (AIM) program can help you launch or advance your career. Complete classroom hours for an apprenticeship, earn an industry-recognized certification, or pursue a degree or training credential on the schedule you choose.
Mid’s AIM program emphasizes in-demand skills like welding and CNC programming alongside topics like communication and project management. Our flexible pathways let you choose what’s right for you:
AIM classes are small, offering one-on-one attention. Our connections with area employers lead to internships or apprenticeships that can earn you journeyman status. And our open labs and online courses help you pursue your education while you’re working.
Planning to earn a bachelor’s degree? Starting at Mid and transferring your credits to a four-year school will save you $15,500 on average. We have plastics engineering transfer agreements with Central Michigan University, Ferris State University, and Saginaw Valley State University.
Chart the path that’s right for you. AIM students can complete associate degrees, training credentials, or certificates in different specialties.
More than 600,000 Michiganders work in manufacturing. Mid’s AIM program prepares you to join their ranks and find a fulfilling career.
Some facts from the National Association of Manufacturers:
AIM careers range from hands-on manufacturing roles to engineering positions that develop materials and product designs to support jobs in sales and more. Specific careers may require an associate degree or a bachelor’s degree:
Associate Degree Careers
Bachelor’s Degree Careers
Flexibility Balance school and work at the pace you choose.
Value Starting at Mid can save you over $16,000 off the cost of a bachelor’s degree.
Mid’s AIM program is perfect for working adults, new high school grads, or anyone looking to build a manufacturing career.
Open labs available days and evenings, 8-week courses, and in-demand certifications let you chart your own path. Laddered options build on one another, allowing you to work at your own pace and earn proof of your skills as you work toward an associate degree, training credential, or certificate.
Choose from specializations in automation and robotics, plastics technology, machine tool, welding, or manufacturing management.
Certifications from respected companies and organizations—Snap-on, Starrett, FANUC, American Welding Society, and more—boost your career potential by showing employers the skills you’ve mastered. Earn these certifications alongside your Mid degree or credential.
Mid is affiliated with NC3, the National Coalition of Certification Centers, a national network that develops certifications based on national skills standards. Certifications demonstrate hands-on experience with state-of-the-art tools.
Show you know how to perform precision measurements, the cornerstone of quality in products and services people rely on. Snap-on, Starrett, and NC3 combined their industrial expertise to certify hands-on training on instruments vital to engineering, manufacturing, aerospace, power generation, natural resources and more.
Earning this certification demonstrates proficiency with instruments and methods including:
Demonstrate experience with Snap-on’s advanced electrical monitoring equipment. This certification will offer you an edge in fields like automotive repair, transportation, wind power, manufacturing, HVAC, and robotics.
You’ll learn to solve problems using digital multimeters, from basic applications to advanced troubleshooting. You’ll build some of the most requested skills in the industry, including:
Get hands-on training with industrial control equipment—learn to use a PLC, specifics of the PLC programming environment, and programming languages. Certification covers:
Understand electricity and how to use it safely. Build, test, and troubleshoot AC/DC circuits and examine operating voltages and currents that impact circuit operation. You’ll learn about:
Learn about construction, operation, and maintenance of hydraulic components, including fundamental principles and valves controlling pressure, flow, rate, sequence, and direction. Practical exercises cover topics like:
Show you’re ready to enter the workforce safely. Build a foundation in OSHA General Industry Standards, general industry principles, and areas of industry that present the most hazards.
Learn to handle programming responsibilities for FANUC robots.
Develop skills focused on FANUC robot vision and censors.
Build entry-level experience with tool identification and standard safety procedures.
Mid incorporates AWS SENSE—a set of minimum standards and guidelines for welding education programs—into its welding curriculum, ensuring you’ll receive a consistent, comprehensive education. Completing SENSE Level I certification recognizes you as a skilled entry-level welder.

- Josh
Get ready to become an apprentice in just one semester, your tuition covered by Michigan Works. You’ll take four courses on terminology, communication, math, and safety—credits you can later apply to an AIM training credential or associate degree.
Just 14 spots are available each semester. Learn more and apply now.
Mid offers skilled-trades education for virtually every goal or schedule. Complete a career-oriented credential or degree. Earn a Commercial Drivers License. Or pursue short-term training in drone operation, precision measurement, electrical, or welding.